Event-driven continuous-time multiagent model#
The spatial rock-paper-scissors (RPS) is an ABM with the following rules:
Agents can be any of three “kinds”: Rock, Paper, or Scissors.
Agents live in a 2D periodic grid space allowing only one agent per cell.
When an agent activates, it can do one of three actions:
Attack: choose a random nearby agent and attack it. If the agent loses the RPS game it gets removed.
Move: choose a random nearby position. If it is empty move to it, otherwise swap positions with the agent there.
Reproduce: choose a random empty nearby position (if any exist). Generate there a new agent of the same type.
using Agents
using Random
using LinearAlgebra
using Base64
using Agents.DataFrames
using CairoMakie
CairoMakie.activate!(px_per_unit = 1.0)
Update message: Agents v6
This is a new major version of Agents.jl with lots of cool stuff!
However, from this version onwards, we will stop posting update messages
to the REPL console!
If you want to be updated, follow this discourse post:
https://discourse.julialang.org/t/agents-jl-v6-releases-announcement-post/111678
(and see the CHANGELOG.md file online for a list of changes!)
The helper function is adapted from Agents.abmvideo and correctly displays animations in Jupyter notebooks
function abmvio(model;
dt = 1, framerate = 30, frames = 300, title = "", showstep = true,
figure = (size = (600, 600),), axis = NamedTuple(),
recordkwargs = (compression = 23, format ="mp4"), kwargs...
)
# title and steps
abmtime_obs = Observable(abmtime(model))
if title ≠ "" && showstep
t = lift(x -> title*", time = "*string(x), abmtime_obs)
elseif showstep
t = lift(x -> "time = "*string(x), abmtime_obs)
else
t = title
end
axis = (title = t, titlealign = :left, axis...)
# First frame
fig, ax, abmobs = abmplot(model; add_controls = false, warn_deprecation = false, figure, axis, kwargs...)
resize_to_layout!(fig)
# Animation
Makie.Record(fig; framerate, recordkwargs...) do io
for j in 1:frames-1
recordframe!(io)
Agents.step!(abmobs, dt)
abmtime_obs[] = abmtime(model)
end
recordframe!(io)
end
end
abmvio (generic function with 1 method)
Define rock, paper, and scissors (RPS) agents. One can use variant(agent) to see the agent type.
@agent struct Rock(GridAgent{2}) end
@agent struct Paper(GridAgent{2}) end
@agent struct Scissors(GridAgent{2}) end
@multiagent RPS(Rock, Paper, Scissors)
Agent actions
function attack!(agent, model)
# Randomly pick a nearby agent
contender = random_nearby_agent(agent, model)
isnothing(contender) && return # do nothing if there isn't anyone nearby
# The attacking action will be dispatched to the following methods.
attack!(variant(agent), variant(contender), contender, model)
return nothing
end
attack!(::AbstractAgent, ::AbstractAgent, contender, model) = nothing
attack!(::Rock, ::Scissors, contender, model) = remove_agent!(contender, model)
attack!(::Scissors, ::Paper, contender, model) = remove_agent!(contender, model)
attack!(::Paper, ::Rock, contender, model) = remove_agent!(contender, model)
attack! (generic function with 5 methods)
Move actions use move_agent! and swap_agents! functions
function move!(agent, model)
rand_pos = random_nearby_position(agent.pos, model)
if isempty(rand_pos, model)
move_agent!(agent, rand_pos, model)
else
occupant_id = id_in_position(rand_pos, model)
occupant = model[occupant_id]
swap_agents!(agent, occupant, model)
end
return nothing
end
move! (generic function with 1 method)
Reproduce actions use replicate! function
function reproduce!(agent, model)
pos = random_nearby_position(agent, model, 1, pos -> isempty(pos, model))
isnothing(pos) && return
# pass target position as a keyword argument
replicate!(agent, model; pos)
return nothing
end
reproduce! (generic function with 1 method)
Defining the propensity (“rate” in Gillespie stochastic simulations) and timing of the events
attack_propensity = 1.0
movement_propensity = 0.5
reproduction_propensity(agent, model) = cos(abmtime(model))^2
reproduction_propensity (generic function with 1 method)
Register events with AgentEvent
attack_event = AgentEvent(action! = attack!, propensity = attack_propensity)
reproduction_event = AgentEvent(action! = reproduce!, propensity = reproduction_propensity)
Agents.AgentEvent{typeof(Main.var"##230".reproduce!), typeof(Main.var"##230".reproduction_propensity), DataType, typeof(Agents.exp_propensity)}(Main.var"##230".reproduce!, Main.var"##230".reproduction_propensity, Agents.AbstractAgent, Agents.exp_propensity)
We want a different distribution other than exponential distribution for movement time
function movement_time(agent, model, propensity)
# Make time around 1
t = 0.1 * randn(abmrng(model)) + 1
return clamp(t, 0, Inf)
end
movement_time (generic function with 1 method)
Also rocks do not move
movement_event = AgentEvent(
action! = move!, propensity = movement_propensity,
types = Union{Scissors, Paper}, timing = movement_time
)
Agents.AgentEvent{typeof(Main.var"##230".move!), Float64, Union, typeof(Main.var"##230".movement_time)}(Main.var"##230".move!, 0.5, Union{Main.var"##230".Paper, Main.var"##230".Scissors}, Main.var"##230".movement_time)
Collect all events
events = (attack_event, reproduction_event, movement_event)
(Agents.AgentEvent{typeof(Main.var"##230".attack!), Float64, DataType, typeof(Agents.exp_propensity)}(Main.var"##230".attack!, 1.0, Agents.AbstractAgent, Agents.exp_propensity), Agents.AgentEvent{typeof(Main.var"##230".reproduce!), typeof(Main.var"##230".reproduction_propensity), DataType, typeof(Agents.exp_propensity)}(Main.var"##230".reproduce!, Main.var"##230".reproduction_propensity, Agents.AbstractAgent, Agents.exp_propensity), Agents.AgentEvent{typeof(Main.var"##230".move!), Float64, Union, typeof(Main.var"##230".movement_time)}(Main.var"##230".move!, 0.5, Union{Main.var"##230".Paper, Main.var"##230".Scissors}, Main.var"##230".movement_time))
Model function EventQueueABM for an event-driven ABM
const alltypes = (Rock, Paper, Scissors)
function initialize_rps(; n = 100, nx = n, ny = n, seed = 42)
space = GridSpaceSingle((nx, ny))
rng = Xoshiro(seed)
model = EventQueueABM(RPS, events, space; rng, warn = false)
for p in positions(model)
# Randomly assign one of the agent
type = rand(abmrng(model), alltypes)
add_agent!(p, constructor(RPS, type), model)
end
return model
end
initialize_rps (generic function with 1 method)
Have a look at the event queue
model = initialize_rps()
abmqueue(model)
DataStructures.BinaryHeap{Pair{Tuple{Int64, Int64}, Float64}, Base.Order.By{typeof(last), DataStructures.FasterForward}}(Base.Order.By{typeof(last), DataStructures.FasterForward}(last, DataStructures.FasterForward()), [(6080, 1) => 2.9790681020079457e-6, (3987, 1) => 0.0003364593569030146, (6221, 2) => 0.0004887948187761659, (8424, 1) => 0.0006778319693496694, (5035, 1) => 0.0012044922191219774, (7014, 2) => 0.0005771225059120387, (3301, 2) => 0.0011396494447446436, (2505, 1) => 0.0014309955844005063, (5041, 2) => 0.001449028423933035, (5539, 2) => 0.0024520873429744127 … (9990, 1) => 1.0666363792018059, (9992, 2) => 0.7429399475482082, (9993, 1) => 1.9378465659189394, (4997, 1) => 1.7907183401427267, (2496, 1) => 0.5304394096759053, (2499, 1) => 2.7442278746073216, (4998, 3) => 1.0804360033507288, (4999, 1) => 5.80807081086072, (9998, 1) => 0.9433255253597445, (1250, 3) => 1.258669914970242])
The time in EventQueueABM is continuous, so we can pass real-valued time.
step!(model, 123.456)
nagents(model)
9716
The step! function also accepts a terminating condition.
function terminate(model, t)
willterm = length(allagents(model)) < 5000
return willterm || (t > 1000.0)
end
model = initialize_rps()
step!(model, terminate)
abmtime(model)
1000.0000727740552
Data collection#
adata: aggregated data to extract information from the execution stats
adf: agent data frame
model = initialize_rps()
adata = [(a -> variantof(a) === X, count) for X in alltypes]
adf, mdf = run!(model, 100.0; adata, when = 0.5, dt = 0.01)
adf[1:10, :]
| Row | time | count_#23_X=Main.var"##230".Rock | count_#23_X=Main.var"##230".Paper | count_#23_X=Main.var"##230".Scissors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float64 | Int64 | Int64 | Int64 | |
| 1 | 0.0 | 3293 | 3372 | 3335 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 3226 | 3262 | 3156 |
| 3 | 1.0 | 3266 | 3202 | 3002 |
| 4 | 1.5 | 3184 | 3109 | 2839 |
| 5 | 2.0 | 3093 | 2987 | 2644 |
| 6 | 2.51 | 2959 | 2879 | 2421 |
| 7 | 3.02 | 2934 | 2849 | 2288 |
| 8 | 3.53 | 3068 | 2968 | 2348 |
| 9 | 4.04 | 3221 | 3034 | 2392 |
| 10 | 4.55 | 3251 | 3058 | 2358 |
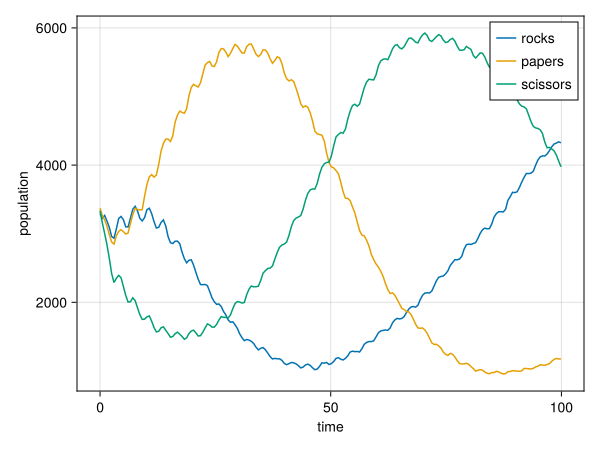
Visualize population change#
tvec = adf[!, :time] ## time as x axis
populations = adf[:, Not(:time)] ## agents as data
alabels = ["rocks", "papers", "scissors"]
fig = Figure();
ax = Axis(fig[1,1]; xlabel = "time", ylabel = "population")
for (i, l) in enumerate(alabels)
lines!(ax, tvec, populations[!, i]; label = l)
end
axislegend(ax)
fig
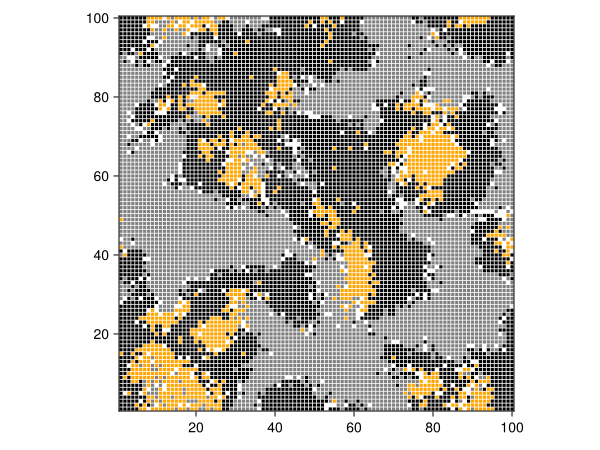
Visualize agent distribution#
const colormap = Dict(Rock => "black", Scissors => "gray", Paper => "orange")
agent_color(agent) = colormap[variantof(agent)]
plotkw = (agent_color, agent_marker = :rect, agent_size = 5)
fig, ax, abmobs = abmplot(model; plotkw...)
fig
Animation#
model = initialize_rps()
vio = abmvio( model;
dt = 0.5, frames = 300,
title = "Rock Paper Scissors (event based)",
plotkw...,
)
save("rps.mp4", vio)
vio |> display
This notebook was generated using Literate.jl.