COVID-19 social distancing model#
This continuous space model assumes people as circles bumping each other to simulate infection process. Source: Agents.jl model zoo
using Agents
using Random
using Base64
using CairoMakie
CairoMakie.activate!(px_per_unit = 1.0)
Update message: Agents v6
This is a new major version of Agents.jl with lots of cool stuff!
However, from this version onwards, we will stop posting update messages
to the REPL console!
If you want to be updated, follow this discourse post:
https://discourse.julialang.org/t/agents-jl-v6-releases-announcement-post/111678
(and see the CHANGELOG.md file online for a list of changes!)
The helper function is adapted from Agents.abmvideo and correctly displays animations in Jupyter notebooks
function abmvio(model;
dt = 1, framerate = 30, frames = 300, title = "", showstep = true,
figure = (size = (600, 600),), axis = NamedTuple(),
recordkwargs = (compression = 23, format ="mp4"), kwargs...
)
# title and steps
abmtime_obs = Observable(abmtime(model))
if title ≠ "" && showstep
t = lift(x -> title*", time = "*string(x), abmtime_obs)
elseif showstep
t = lift(x -> "time = "*string(x), abmtime_obs)
else
t = title
end
axis = (title = t, titlealign = :left, axis...)
# First frame
fig, ax, abmobs = abmplot(model; add_controls = false, warn_deprecation = false, figure, axis, kwargs...)
resize_to_layout!(fig)
# Animation
Makie.Record(fig; framerate, recordkwargs...) do io
for j in 1:frames-1
recordframe!(io)
Agents.step!(abmobs, dt)
abmtime_obs[] = abmtime(model)
end
recordframe!(io)
end
end
abmvio (generic function with 1 method)
Let us first create a simple model where balls move around in a continuous space. We need to create agents that comply with ContinuousSpace, i.e. they have a pos and vel fields, both of which are tuples of float numbers.
@agent struct SocialAgent(ContinuousAgent{2, Float64})
mass::Float64
end
Ball collision model
function ball_model(; speed=0.002, seed=42, model_step! = (m)->nothing)
space2d = ContinuousSpace((1, 1); spacing = 0.02)
rng = MersenneTwister(seed)
model = StandardABM(SocialAgent, space2d; agent_step!, model_step!, properties = Dict(:dt => 1.0), rng)
for i in 1:500
pos = Tuple(rand(rng, 2))
vel = sincos(2π * rand(rng)) .* speed
mass = 1.0
add_agent!(pos, model, vel, mass)
end
return model
end
ball_model (generic function with 1 method)
Move the agent in a continuous space
agent_step!(agent, model) = move_agent!(agent, model, model.dt)
agent_step! (generic function with 1 method)
Visualization (I)#
vio = abmvio(
ball_model();
title="Ball Model", agent_size=10,
frames=100, dt=2, framerate=25,
)
save("social1.mp4", vio)
vio |> display
As you can see the agents move in a straight line in a periodic space without interactions. Let’s change that.
Billiard-like interaction#
We can simulate agent collisions using the API:
interacting_pairs(m, radius, method)elastic_collision!(a1, a2, :mass)
And we redefine the model stepping function with elastic collision:
function model_step!(model)
for (a1, a2) in interacting_pairs(model, 0.010, :nearest)
elastic_collision!(a1, a2, :mass)
end
end
vio = abmvio(
ball_model(;model_step!);
title="Billiard-like", agent_size=10,
frames=100, dt=2, framerate=25,
)
save("social2.mp4", vio)
vio |> display
Immovable agents#
For the following social distancing example, it will become crucial that some agents don’t move, and can’t be moved (i.e. they stay “isolated”). This is very easy to do with the elastic_collision! function, we only have to make some agents have infinite mass.
model3 = ball_model(;model_step!)
for i in 1:400
agent = model3[i]
agent.mass = Inf
agent.vel = (0.0, 0.0)
end
vio = abmvio(
model3;
title="Billiard-like with stationary agents",
agent_size=10,
frames=100, dt=2, framerate=25,
)
save("social3.mp4", vio)
vio |> display
Virus spread (SIR model)#
The agents can be infected with a disease and transfer the disease to other agents around them.
@agent struct SIRAgent(ContinuousAgent{2, Float64})
mass::Float64 ## Movable or not
days_infected::Int ## number of days since is infected
status::Symbol ## :S, :I or :R
β::Float64 ## Transmission rate
end
const steps_per_day = 24
function sir_initiation(;
infection_period = 30 * steps_per_day,
detection_time = 14 * steps_per_day,
reinfection_probability = 0.05,
isolated = 0.0, ## in percentage
interaction_radius = 0.012,
dt = 1.0,
speed = 0.002,
death_rate = 0.044,
N = 1000,
initial_infected = 5,
seed = 42,
βmin = 0.4,
βmax = 0.8,
)
properties = (;
infection_period,
reinfection_probability,
detection_time,
death_rate,
interaction_radius,
dt,
)
space = ContinuousSpace((1,1); spacing = 0.02)
model = StandardABM(SIRAgent, space, agent_step! = sir_agent_step!,
model_step! = sir_model_step!, properties = properties,
rng = MersenneTwister(seed))
# Add initial individuals
for ind in 1:N
pos = Tuple(rand(abmrng(model), 2))
status = ind ≤ N - initial_infected ? :S : :I
isisolated = ind ≤ isolated * N
mass = isisolated ? Inf : 1.0
vel = isisolated ? (0.0, 0.0) : sincos(2π * rand(abmrng(model))) .* speed
β = (βmax - βmin) * rand(abmrng(model)) + βmin
add_agent!(pos, model, vel, mass, 0, status, β)
end
return model
end
sir_initiation (generic function with 1 method)
Stepping functions
function transmit!(a1, a2, reinfectprob, model)
# for transmission, only 1 can have the disease (otherwise nothing happens)
count(a.status == :I for a in (a1, a2)) ≠ 1 && return nothing
infected, healthy = a1.status == :I ? (a1, a2) : (a2, a1)
rng = abmrng(model)
rand(rng) > infected.β && return nothing
if healthy.status == :R
rand(rng) > reinfectprob && return nothing
end
healthy.status = :I
return nothing
end
function recover_or_die!(agent, model)
if agent.days_infected ≥ model.infection_period
if rand(abmrng(model)) ≤ model.death_rate
remove_agent!(agent, model)
else
agent.status = :R
agent.days_infected = 0
end
end
return nothing
end
function sir_model_step!(model)
r = model.interaction_radius
for (a1, a2) in interacting_pairs(model, r, :nearest)
transmit!(a1, a2, model.reinfection_probability, model)
elastic_collision!(a1, a2, :mass)
end
return nothing
end
update!(agent) = agent.status == :I && (agent.days_infected += 1)
function sir_agent_step!(agent, model)
move_agent!(agent, model, model.dt)
update!(agent)
recover_or_die!(agent, model)
end
sir_agent_step! (generic function with 1 method)
Visualize the initial condition
sir_model = sir_initiation()
StandardABM with 1000 agents of type SIRAgent
agents container: Dict
space: periodic continuous space with [1.0, 1.0] extent and spacing=0.02
scheduler: fastest
properties: infection_period, reinfection_probability, detection_time, death_rate, interaction_radius, dt
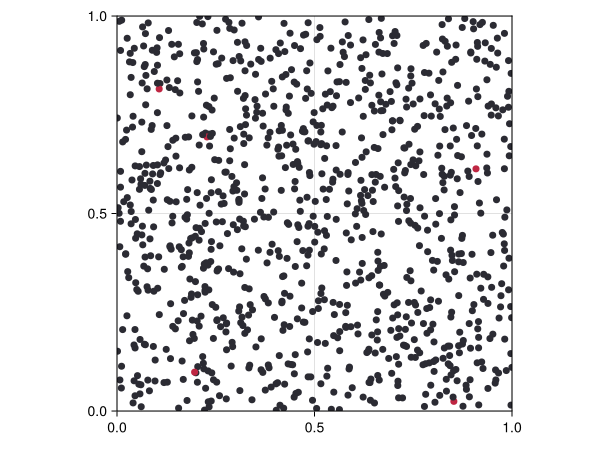
S = black; I = red; R = green
sir_colors(a) = a.status == :S ? "#2b2b33" : a.status == :I ? "#bf2642" : "#338c54"
sir_colors (generic function with 1 method)
Plot figure
fig, ax, abmp = abmplot(sir_model; agent_color = sir_colors, agent_size = 10)
fig
Animation time
sir_model = sir_initiation()
vio = abmvio(
sir_model;
title = "SIR model",
frames = 80,
agent_color = sir_colors,
agent_size = 10,
dt = 1,
framerate = 20,
)
save("social4.mp4", vio)
vio |> display
Analyzing exponential spread#
infected(x) = count(i == :I for i in x)
recovered(x) = count(i == :R for i in x)
adata = [(:status, infected), (:status, recovered)]
2-element Vector{Tuple{Symbol, Function}}:
(:status, Main.var"##230".infected)
(:status, Main.var"##230".recovered)
Try different parameters
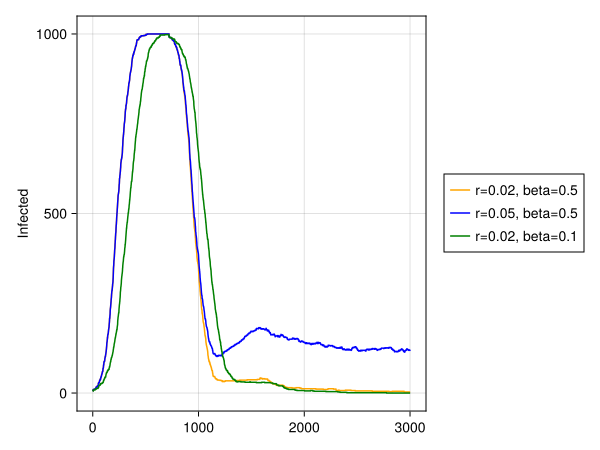
r1, r2 = 0.02, 0.05
β1, β2 = 0.5, 0.1
sir_model1 = sir_initiation(reinfection_probability=r1, βmax=β1)
sir_model2 = sir_initiation(reinfection_probability=r2, βmax=β1)
sir_model3 = sir_initiation(reinfection_probability=r1, βmax=β2)
data1, _ = run!(sir_model1, 3000; adata)
data2, _ = run!(sir_model2, 3000; adata)
data3, _ = run!(sir_model3, 3000; adata)
data1[(end-10):end, :]
| Row | time | infected_status | recovered_status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Int64 | Int64 | Int64 | |
| 1 | 2990 | 3 | 940 |
| 2 | 2991 | 3 | 940 |
| 3 | 2992 | 3 | 940 |
| 4 | 2993 | 3 | 940 |
| 5 | 2994 | 3 | 940 |
| 6 | 2995 | 3 | 940 |
| 7 | 2996 | 3 | 940 |
| 8 | 2997 | 3 | 940 |
| 9 | 2998 | 3 | 940 |
| 10 | 2999 | 3 | 940 |
| 11 | 3000 | 3 | 940 |
figure = Figure()
ax = figure[1, 1] = Axis(figure; ylabel = "Infected")
l1 = lines!(ax, data1[:, dataname((:status, infected))], color = :orange)
l2 = lines!(ax, data2[:, dataname((:status, infected))], color = :blue)
l3 = lines!(ax, data3[:, dataname((:status, infected))], color = :green)
figure[1, 2][1,1] = Legend(figure, [l1, l2, l3], ["r=$r1, beta=$β1", "r=$r2, beta=$β1", "r=$r1, beta=$β2"])
figure
Social distancing#
The simplest way to model social distancing is to make some agents stationary. Here we make 80% of the agents not move.
Compare the number of infected agents for different parameters.
This notebook was generated using Literate.jl.